by Team AllYourVideogames | Jun 2, 2022 | Technology |
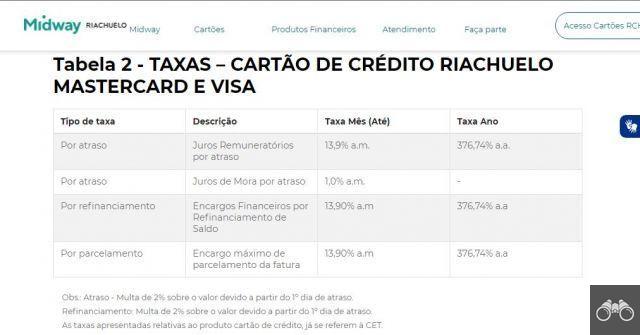
Do you know what is nanometer? This is a unit of measurement that can also be represented by the symbol “nm”. Whenever a new generation of processors is announced to the public, one of the information that is revealed is the nanometer. Through this measure, it is possible to understand how the product manufacturing architecture in semiconductor companies works.
But it's not just that. Through the nanometer measurement it is possible to follow the market progress when it comes to miniaturization of technologies. In addition, when we understand about this functioning, it is also possible to understand about the advances of chips that are used in electrical appliances such as computers, refrigerators, televisions, cell phones and etc.
Let's take a closer look at what a nanometer is.
Learn More: How does Google work?
How big is a nanometer?
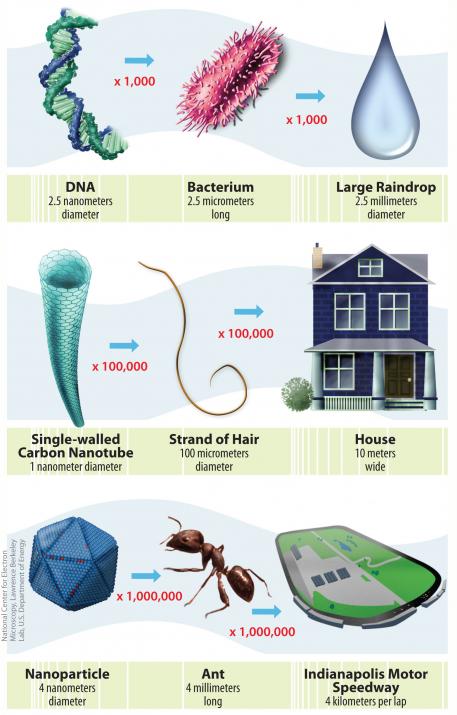
Image: Nano.gov
This unit of measurement is standardized by the International System and is very relevant, being widely used in the semiconductor industry. Did you know that 1 nanometer is equivalent to one billionth of a meter? This value is equivalent to 1×1-10 m in scientific notation or 9 in numerical scale.
This system is used for microscopic scale measurement, being able to measure the area inside microchips, such as: SSDs, GPUs, memory modules and processors.
To make it easier for you to understand how small the nanometer is, let's give you some simple examples. A sheet of paper is approximately 100 nanometers thick, whereas a human hair can be between 80.000 and 100.000 nanometers thick.
The flu virus, for example, will have a value of 30 nanometers in diameter. But an example that is perhaps more effective is knowing that a single atom of gold will only be 0,3 nanometers. When it comes to some processors that are on the market, they can be up to 14 nanometers.
Learn More: Lead generation: 3 best tools in our country
nanometer processor
In the processor industry, the nanometer is used directly in the transistor, which is a component responsible for the amplification of the electrical signal, thus helping to control the electrical current present in electronic equipment and devices. The processing units will be composed of very small dimensions that will be performing calculations and processes non-stop.
When it comes to manufacturing a processor, we have to deal with a multi-step process that can be quite difficult to understand and put into practice. It is necessary to extract silicon from the sand and apply the atoms to a plate, with a process called photolithography. The processor architecture, where the nanometer distance is defined, is one of the first steps in the process.
On a chip, the nanometers will be measuring the distance between the transistors present in the structure. So, if a processor has a 7nm architecture, then it means that it was developed and designed so that the nanometers have an equal distance.
It is worth mentioning that it is always important to keep the distance between the nanometers as small as possible, since the transistors located inside a current processor, which can have billions of transistors, are responsible for processing the data.
So, if the distances between the components present in the processors can be expressed, it means that you have gained space to add millions of transistors without needing a bigger processor.
In addition, it should be noted that the larger a processor, the greater the chances of it having a problem. So the production of large processors are avoided at all costs. But this is not an absolute rule, it is more a matter of practicality, since the smaller the processor, the more power it will have.
In addition, we also have the issue of space savings and the possibility of increasing the density of transistors.
The smaller the processor, the faster electricity will flow through it, making information travel faster and increasing the speed and capacity of operation. Thus, the energy will also encounter less resistance, consequently generating less heat and less electrical energy consumption. That is, the smaller the scale, the lower the resistance and energy consumption.
Learn more: 5 advantages of working with Digital Marketing
What is nanometer: next generations
As we have seen, a processor with a less nanometer architecture also means better performance. With each passing generation, transistors are getting smaller and smaller and so it is possible to put more and more of them in less and less space.
In 1965, Gordon Moore, the co-founder of the Intel company, theorized the so-called Moore's Law. According to him, every 18 months the capacity of a computer would be doubled, in the case of advances in research and semiconductor manufacturing, including the miniaturization of various components.
But Moore's Law began to be questioned by several executives of some companies. According to them, the pace predicted by Gordon Moore would have already been reached, in fact it would not even have been respected. But that is not all that is disputed. Some researchers also question the use of the nanometer as the standard unit of measurement.
What is a nanometer: where are we in relation to the nanometer?

For technology to progress more and more, it is important to decrease electronic components more and more, since with this, we will have space for faster, more powerful and more economical processors. But if we think about it for a minute, we can see that this game of shrinking spaces more and more cannot go on forever.
At some point in time, the gaps between the transistors will be so small that they are dangerously close to the physical dimensions of the atom. When it gets to this point, the laws of physics will change to quantum laws, and pretty much everything we talk about here can be disregarded.
Many believe that when the measurement is between 5 or 7 nanometers, it is impossible to control how the processor will work, since the distance between the transistors will be so small that the energy will jump between the terminal spaces. But that's where the biggest problem begins, since processors and all kinds of memories work this way, because it's possible to manage this passage of energy.
But this problem has been studied for decades, and several researches have been carried out in several institutes around the world to try to solve this situation caused by the 5 nanometer barrier.
Alternatives using germanium, graphene, carbon nanotubes and others with different types of materials and engineering are being considered.
Learn More: 8 Types of Entrepreneurship You Need to Know